7 Organs You Don’t Really Need To Survive
Did you know that we have some internal organs that we don’t even need to survive?
The human body is a system that never ceases to surprise the scientific community. It is very complex and its functions can vary from person to person, and to put it mildly, it has a few fascinating features.
Despite the fact that each body performs a specific function, some of them are not irreplaceable in terms of survival, for example in the event of an accident or illness.
Do you know what these bodies are? In this article we want to tell you about them!
You can do without these internal organs
1. Throat
The tonsils are part of our defense system that we don’t need to stay alive. They help protect bacteria from entering our bodies at the beginning of the airways, but after three years of age, they are no longer vital to us.
Some people even believe that removing tonsils at a young age will prevent future health problems. Doctors, on the other hand, recommend the removal of tonsils when a patient suffers from recurrent tonsillitis.
2. Appendicitis
The appendix is a small pouch-shaped organ attached to the colon. It is located in the lower abdomen.
Despite its location, it is not involved in digestion in any way. Actually, it has no established activity of any kind.
- Many people know of its existence when it becomes inflamed, which causes inflammation of the appendix and then it needs to be removed.
- After removal, the patient does not have any negative side effects and can continue to live without ailments. So this is one of those internal organs that can do without.
3. Perna
The spleen is located in the abdominal cavity and has essential health functions: filtering blood and fighting inflammation.
Nevertheless, the spleen is not vital and can be removed in the event of injury or chronic illness. The patient can continue a normal life as long as a few precautions are taken to avoid inflammation.
4. Genitals
The genitals such as the ovaries, uterus and testicles perform certain functions. Nevertheless, they can be removed as part of the treatment of some chronic disease.
In many cases, doctors recommend removing them to prevent or eliminate cancer. However, the cause may also be a recommendation for the treatment of some other symptoms.
The removal of these organs usually does not cause major after-effects and the hormone deficiencies caused by the removal of the genitals can be compensated by taking hormone therapy.
5. Kidney
There is no denying that the kidneys are not an important part of whole body health. These organs filter blood, produce urine and work together with other organs.
What’s interesting about the kidneys is that even though there are two, we only need one to survive. We can be born without a kidney, suffer from kidney dysfunction due to an accident or illness, or even surrender another without getting chronic health problems.
- In general, people with only one kidney have a normal life expectancy and suffer very little from the consequences.
- However, certain preventive measures are necessary to keep the kidneys healthy and to avoid possible additional diseases.
6. Gallbladder
The gallbladder is a small, green, pear-shaped pouch hidden behind the liver. Its main function is to store and release bile, which helps in the digestion of food.
However, if the gallbladder is weakened or has complications such as gallstones or cancer, doctors recommend removing it.
- Despite the help of the gallbladder for digestion, life without the gallbladder usually does not cause problems.
- Some patients may experience diarrhea and swelling, but only after eating irritating foods.
7. Abdomen
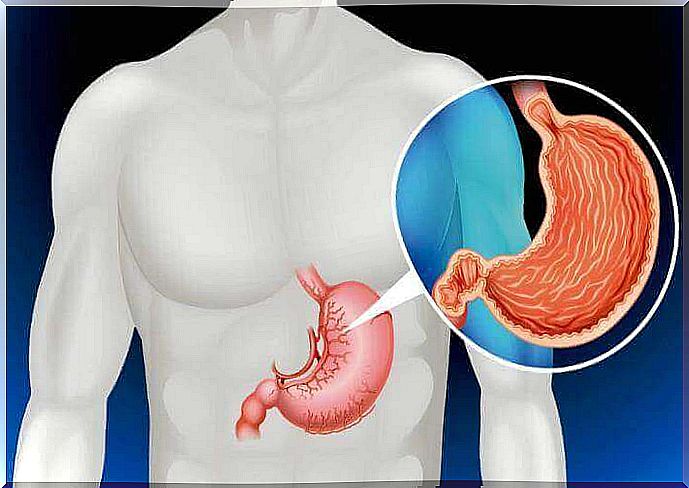
While this may sound incredible, people can survive without a stomach. In fact, there is a surgical procedure called gastrectomy in which the entire stomach is removed due to cancer.
Surgeons connect the small intestine to the esophagus in this procedure. After surgery, the patient is fed through a tube for several weeks until he has fully recovered.
- Due to the complexity of the procedure, patients must follow a very precise treatment program.
- Patients can enjoy most foods, but the amounts should be smaller.
- Dietary supplements are recommended to prevent complications due to food absorption.
As you can see, while it is good to take care of all the internal organs to keep them healthy, we have organs that we do not need to stay alive, but can be removed if necessary. Wonderful, isn’t it?