Low Thyrotropin: Causes And Treatment
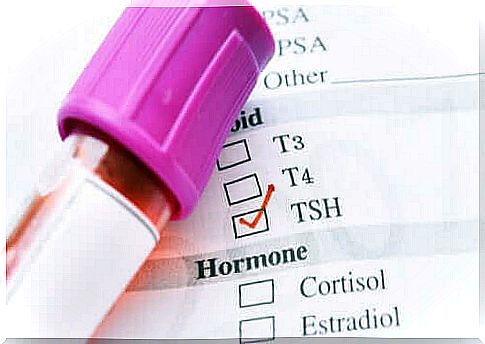
Thyrotropin (TSH) is a molecule involved in thyroid dysfunction. For this reason, doctors require measuring the level of thyrotropin in the blood when they notice some thyroid-related symptoms. In this article, we will explain why low thyrotropin is caused.
Low thyrotropin is a sign of a change that requires further investigation. Indeed, measuring its concentration in the blood is often just one of many studies.
What is thyrotropin or TSH?
TSH comes from the words thyroid-stimulating hormone, a thyroid-stimulating hormone. It is therefore thyrotropin, a hormone that regulates thyroid function. The pituitary gland releases it after receiving a stimulus from the hypothalamus through another hormone, thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), or thyroliberin.
When thyrotropin is in the blood, it attaches to thyroid cells to produce two other hormones:
- T3 or triiodothyronine. This is much more active than T4 and is the hormone that causes effects in tissues i.e. regulates their metabolism.
- T4 or thyroxine. This hormone has little effect on tissues. Rather, it is a reserve of T3, as upon transport to tissues, T4 can be converted to T3, the ultimate active hormone.
T3 and T4 are transported to tissues to regulate the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. In addition, these hormones are very important in babies as they help newborn brain tissue to develop normally.
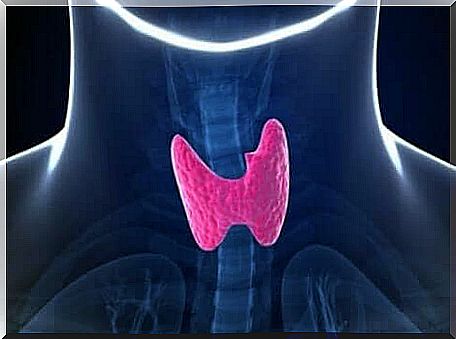
What causes low thyrotropin?
According to a study published in 2017 involving approximately 4,550 people between the ages of 18 and 93, the incidence of hypothyroidism was 9.1%, while the incidence of hyperthyroidism was 0.8%.
Together, these two disorders affect nearly 10 percent of the population, and it would be possible to find a different TSH value in all of these patients. The amount of the hormone in question is regulated by three factors:
- The amount of TRH released by the hypothalamus
- The pituitary gland, which is responsible for storing and releasing TSH when needed
- Negative feedback effect of thyroid hormones
What is the negative feedback effect?
When a lot of thyroid hormones are formed, their amount in the blood increases. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland both detect this increase and reduce the production of TRH and TSH. This is meant by a negative feedback effect.
In other words, hormones regulate themselves to keep their blood levels steady. Without this mechanism, we would constantly go to the side of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
The amount of TSH in the blood
The normal concentration of TSH in the blood is 0.4-4 mIU / L. If the values are higher or lower than this, it is a thyroid dysfunction.
Low thyrotropin means that there is so much T3 and T4 in the blood that the pituitary gland has a negative feedback effect that prevents its production. This is usually an overactive thyroid gland.
Thyrotropin may also be low due to secondary hypothyroidism. This occurs when the pituitary gland is malfunctioning either because it has been partially destroyed or because something – such as a brain tumor – is blocking its normal function.
Tertiary hypothyroidism may also be the cause. This means that the hypothalamus does not function and stops producing TRH, so it does not send a message to the pituitary gland to form TSH.
In the first case, when peripheral thyroid hormones are overproduced, blood levels of T3 and T4 are elevated, indicating that the metabolism is working too hard. This is why the body starts burning fat and sugars to get energy.
Low thyrotropin: treatment
Hyperthyroidism
Some of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism include nervousness, palpitations, hyperactivity, increased sweating, hypersensitivity to heat, increased appetite, and weight loss.
Contact your doctor if you think you are suffering from hyperthyroidism. Your doctor will probably send you for blood tests to look for levels of TSH, T3, and T4. Your doctor will confirm hyperthyroidism if thyrotropin is low and thyroid hormones are elevated.
Causes can range from a thyroid tumor to an autoimmune disease in which the antibodies formed stimulate the thyroid cells too much. There are medications to relieve and control the symptoms.

Hypothyroidism
Opposite symptoms such as fatigue, obesity, impaired cold tolerance, and decreased body temperature are signs of hypothyroidism. The cause may be, for example, a brain tumor that either destroys or presses on the pituitary gland, preventing the release of TSH. It may also be due to low production of T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland itself.
Low thyrotropin in hypothyroidism is a sign of a more serious problem associated with pituitary destruction. If, on the other hand, TSH is normal or elevated, the cause may be suspected thyroid.