Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
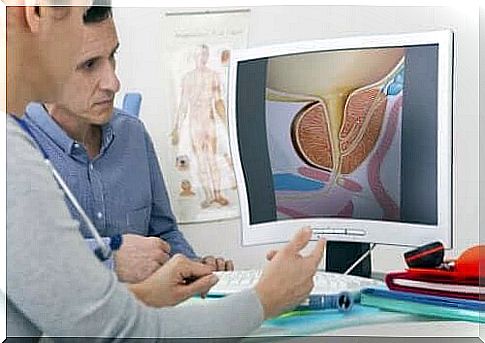
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a medical term that refers to an abnormal increase in the size of a man’s prostate.
First, it is very important to determine whether there is benign prostatic hyperplasia or malignant hyperplasia. Malignant hyperplasia is associated with the growth of cancer cells.
The age of the patient must also be taken into account, as the size of the prostate is not always the same. After the age of 40, the prostate usually enlarges.
For this reason, men older than this who have symptoms of prostate compression should go to a doctor to examine the cause and quality of the discomfort.
How do benign prostatic hyperplasia symptom?

Benign prostatic hyperplasia includes a number of different symptoms. In the case of malignant hyperplasia, prostate cancer, it has some special features that allow for a faster diagnosis.
At the reception, it is not possible to determine whether the hyperplasia is benign or malignant based solely on the patient’s medical history and physical examination. Additional tests are always needed to determine the quality of overgrowth.
The most common symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia are:
- Pain when urinating
- Inability to urinate
- Hematuria or hematuria
- Constant need to urinate, with only small amounts of urine at a time (most common in the evening)
- Feeling that the bladder is not emptying properly
- Urine comes irregularly intermittently or dripping
These symptoms may sometimes be confused with urinary tract infection, which is why it is always important to see a doctor to find out the cause of the problem.
How is the effort examined?
First, the doctor will determine the patient’s symptoms and medical history. In middle-aged men, the prostate should be described, especially if the patient or someone in his or her family has had prostate cancer or other cancers.
The doctor will then perform a comprehensive physical examination, including an anal examination. Through this, it is possible to detect the abnormal size of the prostate by palpation.
Diagnosis is made by a simple test: a prostate-specific antigen (also known as PSA). A blood test is needed to determine this marker . This eliminates the need to expose the patient to other inconvenient or expensive examinations.
In addition, the physician may utilize imaging techniques, of which ultrasound is the primary option. The resolution of other imaging methods may be better, but because radiation in the genital area can adversely affect a man’s fertility, ultrasound is often the best option.
How is benign prostatic hyperplasia treated?
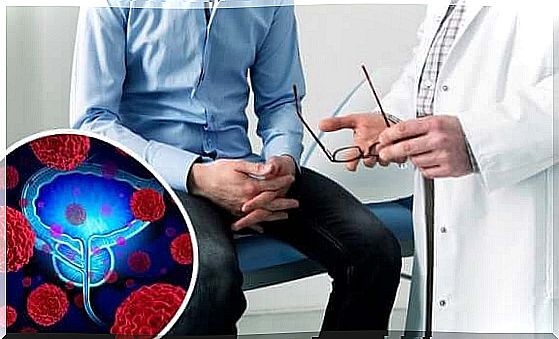
Treatment depends on the quality of the hyperplasia. In benign hyperplasia, compression of other organs by the prostate must be corrected, as the symptoms often have an effect on the patient’s mental state.
Urinary incontinence is the most common reason for middle-aged men to see a urologist. This can be remedied with medication at an early stage.
If the size of the prostate is significant, the excess tissue may need to be removed by surgery. This is the most common option as it is an easy method and gives good results. Another option is to dilate the urethra to facilitate flow or else laser treatment.
In the case of malignant prostatic hyperplasia, the patient is thoroughly examined and tissue samples are taken, among other things, to determine the quality and degree of the cancer and to look for metastases elsewhere in the body (primarily skeletal examination). The patient is often referred to an oncologist.