Chronic Urticaria: Different Types And Their Features

Chronic urticaria, or urticaria, is a skin condition characterized by skin changes that manifest themselves in several different ways. There is typically reddening of the skin and severe itching. According to several studies, an estimated 20% of the world’s population has experienced urticaria at least once in their lifetime.
It is important to know the possible causes of urticaria in order to control it effectively. This is important mainly because of its high prevalence, uncomfortable clinical picture, its various forms, and its epidemiology. In today’s article, we focus on the chronic form of hives.
Incidence of urticaria
Before we can talk about the specifics of any disease, we must first know the dynamics with which the disease manifests itself over time. This is, in fact, one of the first steps in planning treatment and curbing the effort.
An article published in Revista Médica de Buenos Aires provides interesting information on hives:
- An estimated 15-25% of the world’s population has experienced urticaria at least once in their lifetime.
- The incidence of chronic urticaria is in the order of about one percent, meaning that one in every 100 people has it in any population group.
- It occurs as a single case 45 percent of the time, and with angioedema (swelling of the skin) at the rest.
Note at this point that hives are divided into two forms. It is acute when it lasts for up to six weeks, and it is chronic after that. As strange as this may seem, in 80% of cases, little is known about its cause and origin.
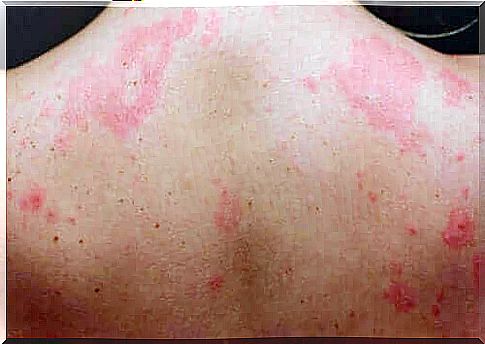
Chronic urticaria: different types
Due to its superficial nature, urticaria may seem like a harmless affliction, but it can still significantly reduce a person’s quality of life. Clinical trials compare the effect of hives with some heart disease.
According to the Asociación de Afectados por la Urticaria Crónica (AAUC), its diverse origins are most often linked to the following processes:
- Autoimmune reactions
- Intolerance and hypersensitivity to some drugs
- Infection processes
- Food allergies
Chronic urticaria is not officially divided into different categories or types, and this has been confirmed by international medical institutions. However, we can classify it according to its causes, the three most common of which are as follows.
Autoimmune reactions
Dermatological studies emphasize that this is the most common cause, as it occurs in an estimated 45% of cases. The body itself activates the skin cells, they release histamine (a compound involved in the immune system), and hives occur.
Other medical review articles emphasize that this mechanism is nevertheless not generally known. The reason is that the trigger that activates antibodies that mediate the immune system is not yet fully understood. About 15 percent of cases are associated with thyroid diseases (e.g., autoimmune thyroiditis).
Chronic urticaria as a result of infections
Some infectious processes as well as viruses, bacteria and fungi are able to contribute to the onset of chronic urticaria. These include:
- Hepatitis A and B virus
- Spread of streptococci
- Mycobacterial tuberculosis (the bacterium that causes the majority of tuberculosis cases in the world)
- Herpes simplex virus
Of particular note is Helicobacter pylori infection – a bacterium that inhabits the human gastric epithelium and appears to be associated with urticaria. A study by Allergologia et Immunopathologia reported that 71% of the patients with chronic urticaria in the study had this microorganism in their digestive system.
However, in 21 of the 21 patients, there was a significant improvement when the bacterium was eradicated from the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, the clear correlation between these two factors remains obscure.
Medicinal
Several analyzes in the world of science have examined the correlation between drug use and chronic urticaria. This disease can be exacerbated by the use of, for example, aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Chronic urticaria: different forms and their treatment
A review published in ScienceDirect in 2015 includes some of the most effective treatments for chronic urticaria. These are the most important of them:
- First-generation antihistamines such as diphenhydramine
- Acrivastine
- Cetirizine and loratadine (second-generation alternatives that are less fatigue)
- Multiple corticosteroids (from which you can choose a drug with a short or long half-life, ie how long it stays in the body)
Most of these drugs seek to alter the response of the immune system and reduce the inflammatory process. Depending on the underlying cause of the disease (which is difficult to identify), more than one medicine may be needed at the same time.
What about chronic urticaria should be kept in mind
As you can see, chronic urticaria is a disease that still involves many open questions today. The scientific community is still unfamiliar with its exact causes and the most effective treatments.
In any case, it should be understood that any rash lasting more than six weeks is a clinical manifestation of chronic urticaria. For this reason, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible to start treatment, as treatment is necessary in these cases. Your doctor may advise you on some general measures to relieve the irritating symptoms and possibly even prescribe medication.