Laryngitis: Causes And Symptoms

Laryngitis can be defined as inflammation of the lining of the throat. The larynx is an important area of anatomy as it provides a passage for inhaled and exhaled air. It is also the most important area for phonation, the vocal folds in this area.
According to experts, this pathology is considered acute in those cases where the inflammation heals within a short period of time (either hours or days). If, on the other hand, the symptoms last for more than three weeks, we can already talk about chronic laryngitis.
Laryngitis is a very common disease and in most cases caused by a virus. Therefore, knowing its causes and symptoms is important. In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know about this common and often fortunately harmless respiratory infection.
How is laryngitis distributed in the population?
To treat laryngitis, it is essential that we know better its epidemiology, that is, who it affects and what its incidence is (the number of people infected in a given population). Epidemiological studies on the subject provide us with particularly interesting information on this respiratory infection:
- Acute laryngitis accounts for 15-20 percent of all respiratory diseases.
- In young children, its incidence is 3-6 percent. In other words, about 6 out of every 100 children under the age of 6 suffer from this pathology at some point before the age of six.
- A typical profile of an infected patient is a two-year-old boy who gets inflammation in the fall and winter.
- Acute laryngitis has a clear family component because, according to pediatricians, children with relatives who have previously suffered from laryngitis are three times more likely to develop the disease.
As we have already seen, we are dealing with a pathology that prevails especially in the environments of young children. This is because young children up to the age of six have a higher-than-normal glottis and looser and less fibrous submucosal tissues, which are more susceptible to various infections than adults.
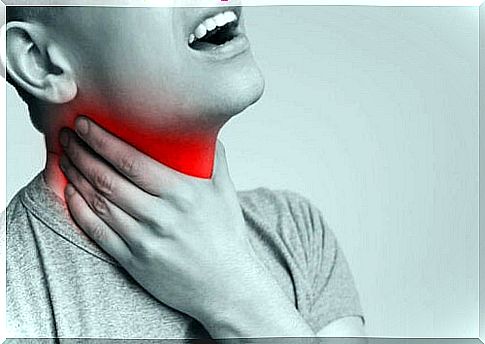
Causes and symptoms of laryngitis
Studies on the subject have identified several causes that can cause laryngitis. These include:
- Infectious: These laryngitis can be caused by viruses (such as influenza, flu, herpes), bacteria (such as mycoplasma and diphtheria) or fungi (such as candidiasis or aspergillosis).
- Non-communicable: These laryngitis are caused by allergies, injuries, medications, or autoimmune diseases.
Viral laryngitis
Studies show that parainfluenza virus types 1, 2 and 3 cause 65% of these cases. Influenza A and B viruses (which cause influenza) as well as different types of adenoviruses are also very common causes of laryngitis.
These pathogens are associated with an infection of the upper respiratory tract that results in typical clinical symptoms of influenza. These include:
- Fever
- Dry throat and sore throat
- Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing
- Breathing difficulties and persistent cough
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Ear pain
These symptoms are due in part to inflammation of the lining of the pharynx, which is red and swollen due to the accumulation of extracellular fluid on the mucous membranes. Treatment is based on resting the patient’s vocal cords and using painkillers to relieve pain and fever.
In acute cases, this disease heals on its own; the progression of the disease stops only a few days after its onset, as the body’s own immune system fights the pathogen, so that the disease does not normally have any sequelae.
Bacterial laryngitis
Bacteria are also a major cause of laryngitis. Like viral inflammation, this form usually heals on its own and relatively quickly, but at the same time, it is good to know what kind of disease it is and why it is caused.
One of the most common causes of this inflammation is bacteria belonging to the genus Mycoplasma, which contain more than 100 different species. The symptoms are very similar to those of viral laryngitis: patients experience fever, dry cough, pain when swallowing, and dysphonia, or loss of voice or hoarseness.
In these cases, the treatment of the disease is based on antibiotics because it is an inflammation caused by a bacterium. Erythromycin, clarithromycin, or azithromycin are effective drugs for killing bacteria in the throat.
Non-infectious laryngitis
In addition to viral and bacterial infections, there are infections of the larynx which are of non-pathogenic origin, ie they do not react to micro-organisms but to the intended use and conditions surrounding the person:
- Allergies: Allergic laryngitis is an acute inflammation of the vocal cords and other laryngeal mucosa due to inhalation of allergens. It has varying symptoms ranging from rough throat to severe airway obstruction.
- Harmful substances that pass through the respiratory tract: In this case, the laryngeal tissues come into direct contact with harmful elements such as smoke or very hot air. This non-infectious form of laryngitis is common in both survivors and firefighters.
- Injury or excessive use of the vocal folds: The larynx may also become irritated as a result of an impact or prolonged and excessive use of the vocal folds.
What should we remember?
Laryngitis is a pathology with a variety of causes, ranging from infectious viruses and bacteria to simple injuries. Regardless of the cause, laryngitis causes many of the same symptoms in patients, such as dysphonia, or hoarseness of voice, and dry cough.
Because infectious pathogens are the most common, they spread between people either in direct contact or through the airways when we are in the same condition as a sick person. For this reason, laryngitis often follows a certain epidemiological pattern, the peaks of which are located in winter and autumn.
These respiratory pathologies are quite common, especially in young children. Fortunately, this is not a serious illness, as the body’s own immune system will sooner or later overcome the disease. However, in cases where the symptoms of the disease last for more than two weeks, it is important that you refer to a doctor to find the correct diagnosis and method of treatment.