Staphylococcal Inflammation: Causes And Symptoms
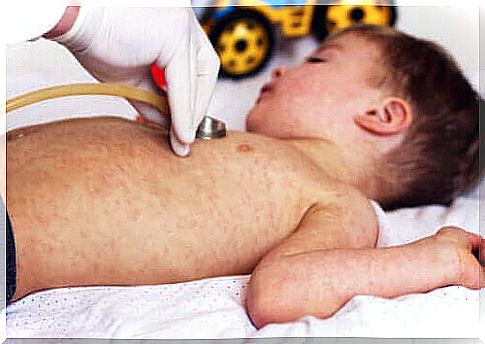
Staphylococcal inflammation is a skin disease that occurs in response to the staphylococcal bacterium. It is characterized by ulcers on the skin and subsequent detachment of the skin.
Newborns and children under 6 years of age are most affected by this disease. The occurrence of staphylococci is indeed rare in adults unless it is associated with immune or renal impairment.
What causes staphylococcal inflammation?
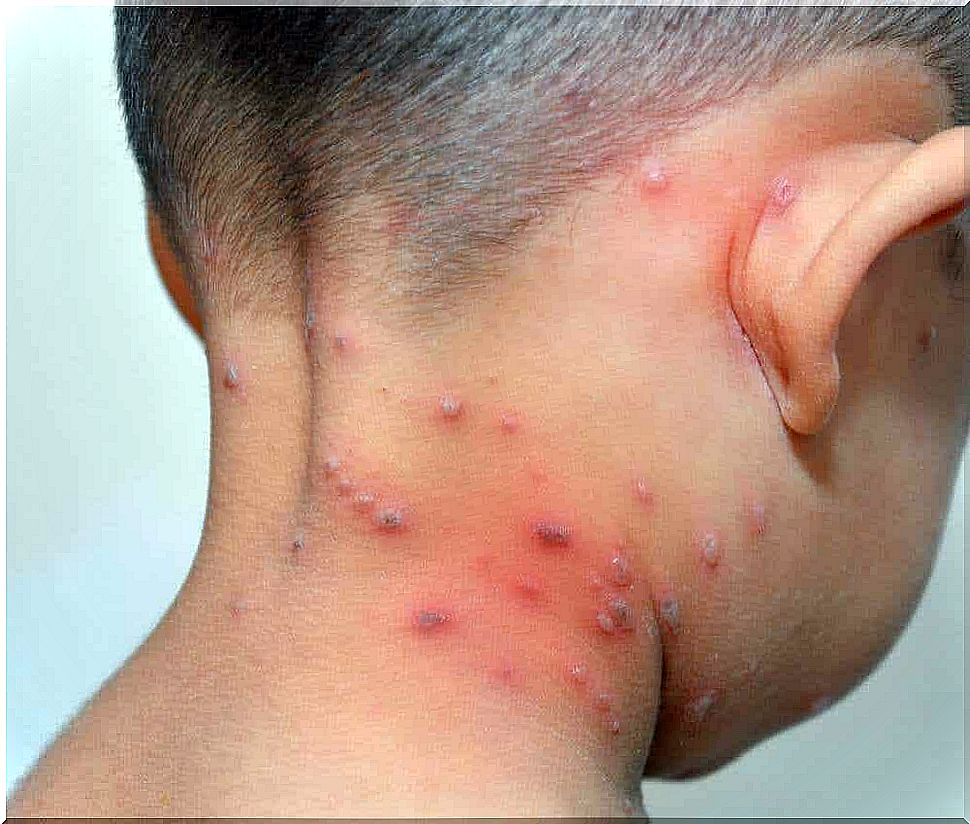
Staphylococcal skin disease is caused by a bacterial variety belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. In most cases, the inflammatory bacterium is Staphylococcus aureus.
These microbes secrete a toxic substance that acts on the skin, causing the outer layer of the epidermis to stand out from the rest of the skin. It results in ulcers and the skin looks burnt.
Most often, the patient initially has an infection that goes unnoticed. When it starts, staphylococcus develops rapidly. Sometimes, however, it may take a few days after the initial infection for the disease to develop.
Staphylococcal dermatitis is contagious. It has increased worldwide since the 1970s. Staphylococcus aureus is estimated to occur in 30-50% of healthy adults.
What are the symptoms of staphylococcus?
Although staphylococcal infection is associated with a number of typical symptoms, each child usually experiences them differently. However, the first symptom is usually a fever with reddening of the skin.
It usually starts with a separate ulcer that scars. In newborns, the ulcer usually appears in the area of the diaper or near the navel. In older children, the ulcer usually always appears on the face and in adults it can start from any part of the body.
The ulcer develops and within 24 hours it turns bright red in color. Shortly thereafter, fluid-containing wet abscesses begin to form. They break easily and leave the skin moist and looking burnt. Other common symptoms include:
- Pain on contact with damaged skin
- Chills
- Vapors
- Dehydration
- Detachment of the superficial layer of the skin from the deeper layers when lightly rubbed. After a few days, the entire skin surface is damaged.
How can the disease be treated?

The diagnosis of staphylococcal inflammation is made based on the clinical picture and the detection of the poison. Sometimes a test piece of skin is needed to confirm the disease. At an early stage, the disease is very similar to smallpox, multiple redness, Kawasaki disease, and the like.
Once the diagnosis has been confirmed by a doctor, treatment is usually started in a hospital. The treatment of this disease is similar to that of burns, and is usually performed in a hospital burn unit. Professionals usually use the following measures:
- The administration of staphylococcal antibiotics is done either orally or intravenously, depending on the patient’s condition. Their job is to prevent infections from spreading.
- Administration of intravenous fluids. The patient loses a lot of fluid from the body through open skin. This requires initiating measures to prevent possible dehydration.
- Skin protection measures. Creams are used to strengthen the skin’s anti-bacterial activity. Moisturizers are also essential.
- Relieving treatments. Cold dressings can be applied to the skin to relieve pain.
Treatments may vary depending on the patient’s age, general health, disease severity, drug tolerance, expectations, and preferences. In most cases, the skin begins to heal 10 days after starting treatment.
How to deal with the disease?
In general, if a child or adult gets treatment in time, there will be no complications. The most significant risk is inflammation of the deeper layer of the skin, which can lead to cellulite. It is also possible that the infection may worsen and enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis.
At the same time, the patient may experience dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. Fever also requires adequate monitoring, especially in newborns. However, if a child or adult receives an early diagnosis of the disease and treatment is started immediately, the outcome is usually good. Staphylococcal inflammation can also be fatal if the patient does not receive appropriate treatment.
Therefore, if you or someone close to you has ulcers that cause a fever and / or any of the other symptoms we mentioned above, see a doctor immediately.